

A seafloor map will show a rather strange pattern of blocky structures that are separated by linear features perpendicular to the ridge axis. These are the fracture zones, many bearing names, that are a major source of submarine earthquakes. Spreading is generally not uniform, so where spreading rates of adjacent ridge blocks are different, massive transform faults occur. Divergent boundaries can create massive fault zones in the oceanic ridge system. The hot spot which may have initiated the Mid-Atlantic Ridge system currently underlies Iceland which is widening at a rate of a few centimeters per year.ĭivergent boundaries are typified in the oceanic lithosphere by the rifts of the oceanic ridge system, including the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Pacific Rise, and in the continental lithosphere by rift valleys such as the famous East African Great Rift Valley. Here, exceedingly large convective cells bring very large quantities of hot asthenospheric material near the surface, and the kinetic energy is thought to be sufficient to break apart the lithosphere. The origin of new divergent boundaries at triple junctions is sometimes thought to be associated with the phenomenon known as hotspots.
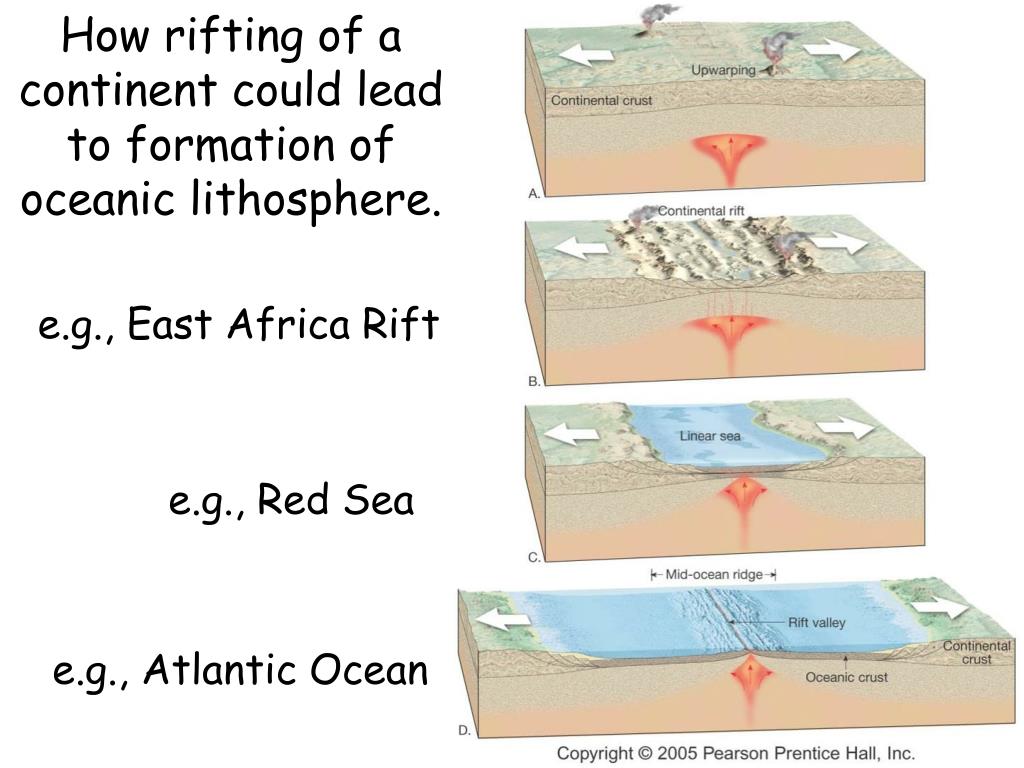

Because of this, rocks closest to a boundary are younger than rocks further away on the same plate.ĭescription File:Bridge across continents iceland.jpgīridge across the Álfagjá rift valley in southwest Iceland, that is part of the boundary between the Eurasian and North American continental tectonic plates.Īt divergent boundaries, two plates move away from each other and the space that this creates is filled with new crustal material sourced from molten magma that forms below. Over millions of years, tectonic plates may move many hundreds of kilometers away from both sides of a divergent plate boundary. Each eruption occurs in only a part of the plate boundary at any one time, but when it does occur, it fills in the opening gap as the two opposing plates move away from each other. This supplies the area with vast amounts of heat and a reduction in pressure that melts rock from the asthenosphere (or upper mantle) beneath the rift area, forming large flood basalt or lava flows. Divergent boundaries also form volcanic islands, which occur when the plates move apart to produce gaps that magma rises to fill.Ĭurrent research indicates that complex convection within the Earth's mantle allows material to rise to the base of the lithosphere beneath each divergent plate boundary. Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys.
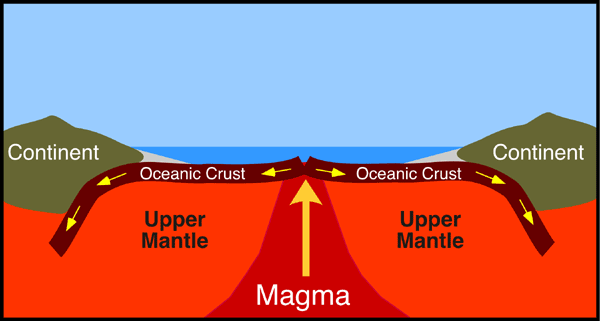
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Template:Short description Template:Pp-pc1 Template:Refimprove File:Continental-continental constructive plate boundary.svgĬontinental-continental divergent/constructive boundary


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
